Google Algorithm Updates in May, July and August

In this post, we will recap recent Google algorithm updates. The most significant update was Google’s “Helpful Content Update” which came in August 2022.
Don’t forget that Google keeps their log of ranking algorithm changes, which you can find here.
Google Helpful Content Update August 2022
This is the most important recent algorithm change from Google.
Recently, on the 18th of August, Google shared information on their upcoming “Helpful Content Update”. This update aims to increase the ranking visibility of ‘people-first’ content, whilst decreasing the rankings of content which is deemed ‘unhelpful’ or which was produced purely to rank within Search Engines (without considering a human audience).
Google reference their “long standing advice and guidelines”, which means that their overall psychology in terms of ‘good content’ hasn’t changed. In a lot of ways, this update is very similar to Google’s prior (and well-known) Panda update (2011 – note that the update wasn’t first named Panda).
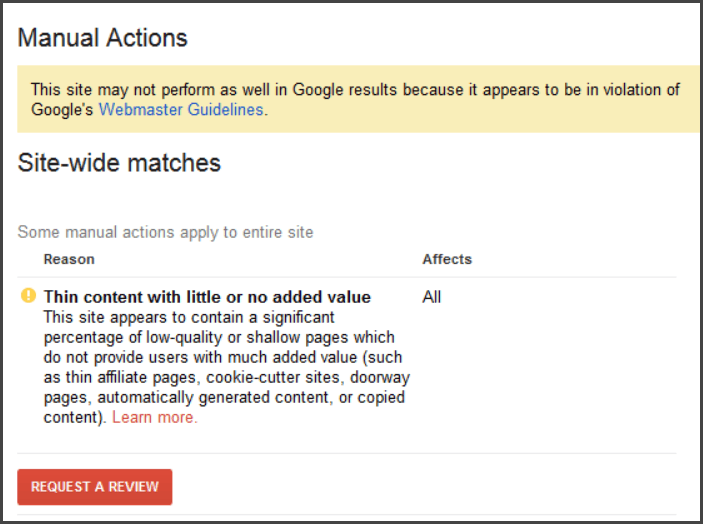
Many of the aims are the same, but the technologies and algorithmic adaptations are different. Panda resulted in raised flags for Google’s manual spam action team. Panda could potentially result in manual actions (also known as ‘penalties’):
By contrast, Google’s “Helpful Content Update” does not relate to manual actions and penalties from the spam team. Instead, unhelpful content will be algorithmically devalued without human involvement.
This is what Google say about their update:
“This classifier process is entirely automated, using a machine-learning model. It is not a manual action nor a spam action. Instead, it’s just a new signal and one of many signals Google evaluates to rank content.
This means that some people-first content on sites classified as having unhelpful content could still rank well if there are other signals identifying that people-first content as helpful and relevant to a query. The signal is also weighted; sites with lots of unhelpful content may notice a stronger effect. In any case, for the best success, be sure you’ve removed unhelpful content and also are following all our guidelines.”
The real difference between Helpful Content and Google’s former update (Panda) is that AI and Machine Learning have now advanced to a point where a manual action team is no longer required.
Additionally, the application of this update is less broad-brush. If websites are flagged as having mostly unhelpful content; an individual piece of content which is very helpful to users – could still rank, in defiance of the norms of the domain’s ranking profile. Though this is true; sites with an abundance of unhelpful (non-useful) content will see a much higher loss of rankings. For sites which are producing mostly unhelpful content, some of their ’helpful’ content may also be impacted.
Let’s try and interpret this in a more human-readable form. Essentially, if a site has some unhelpful content, it will be demoted – but that same site’s helpful content can still rank. However, if a site takes unhelpful content production to an extreme, even pages deemed ‘helpful’ may suffer in Google’s rankings.
So, if you have a few thin pieces of content on-site, a few posts which never really achieved anything… in most instances, there will be no cause for alarm. Those thinner and more unhelpful items of content won’t rank as well (if at all), but largely your site will be unaffected.
On the other hand, if your site automatically concatenates bits of content from across the web to build thin scraped pages – you’ll likely be in for a shock. Even if some of those pages were found useful by searchers, they will also be at risk of demotion.
Google Product Review Update
In late July, Google pushed out an update to encourage users to “write high-quality product reviews”. There’s no change in overall direction from Google here, this is what their guidelines have always stated (they will just be enforcing these guidelines more stringently).
These are some of Google’s top pointers on their update:
- Evaluate the product from a user’s perspective.
- Demonstrate that you are knowledgeable about the products reviewed – show you are an expert.
- Provide evidence such as visuals, audio, or other links of your own experience with the product, to support your expertise and reinforce the authenticity of your review.
- Share quantitative measurements about how a product measures up in various categories of performance.
- Explain what sets a product apart from its competitors.
There are many more recommendations such as potentially including competing products within the review/evaluation. Google has always wanted deeper, user-centric reviews written for an audience. They believe that their recent algorithm update will help to push such reviews within Google’s search results.
The key learning here is to write deeper reviews with the review audience in mind. Instead of just evaluating the product and saying whether it’s good or bad, explore the product. Put the product through some tests, and see how it performs against other competing products. If you use YouTube regularly, you will know that this is the direction in which product review channels have been heading for some time. Google wants to see this in written reviews, also.
Your reviews should add some unique information to the overall body of reviews. If your review simply regurgitates the opinions of others, it probably won’t be highly valued. Reviews don’t have to be overly long, but they should add some unique value-add for users. If they read your review, they should learn something which they don’t already know.
Interestingly there was another product reviews update in May 2022. This more recent July update is likely to be addressing issues with the update from May.
May 2022 Core Update
For some years, Google has been producing ‘core’ ranking updates. Previously updates were more distinct and targeted, for example, the historic Penguin and Panda updates. Nowadays, Google’s updates are usually more intravenous.
Google will still release some smaller named updates (e.g: Helpful Content) but named updates don’t usually have the large and sweeping impacts which they did in years gone by. Google compiles hundreds (if not thousands) of smaller changes into the ‘core’ ranking algorithm. When Google does this, it is known as a core update.
This is what Google has to say about core updates:
“Core updates are changes we make to improve Search overall and keep pace with the changing nature of the web. While nothing in a core update is specific to any particular site, these updates may produce some noticeable changes to how sites perform”
Google doesn’t usually confirm specific alterations during core updates, though the search community will often draw its own conclusions. In this instance, there was lots of very interesting information posted on Search Engine Journal.
It seems as if informational and transactional queries were impacted more heavily than commercial or navigational queries. A tweet from Mordy Oberstein (head of SEO branding at Wix) confirms this. The data itself was originally compiled by Marcus Tober of SEMRush.
In addition to these findings, Steve Paine (Marketing Manager at Sistrix) discovered that generalists were impacted more heavily than topical specialists. An example was given where The Independent saw ranking gains, whilst Daily Mail lost out (due to a difference in topical site architecture).
Overall, we can’t categorically state the alterations or impacts of May’s core algorithm update. What we can say is that content generalists seem to be losing out.
Here at Anicca, we stay up-to-date on all SEO, search and algorithmic developments and apply them to our clients’ campaigns. You can check out our SEO services here. Impressed with our knowledge and coverage of search? Give us a call on 0116 254 7224.